Ethereum Price Forecast: ETH falls below $3,000 as researcher suggests address poisoning is inflating activity
Ethereum price today: $2,980
- Ethereum's network activity surge is likely driven by large-scale address poisoning scams.
- The low-fee environment enabled by the Fusaka upgrade has reduced execution risk for scammers.
- ETH could test the $2,880 support after declining below a key ascending triangle.
Ethereum's (ETH) recent surge in network activity can be traced to increased address poisoning attacks following a decline in gas fees, according to onchain researcher Andrey Sergeenkov.
Last week, daily transaction count spiked to nearly 2.9 million on Friday while weekly active addresses reached a record high. During the period, the network added 2.7 million new addresses, 170% above usual levels, said Sergeenkov. Unlike previous cycles, when such growth often sparked conversations about rising ETH demand and the "ultrasound money" narrative, price remained fairly flat.
However, much of that growth isn't driven by real demand, as address poisoning attackers are taking advantage of the lower fee structure enabled by the Fusaka upgrade to spam users.
Address poisoning attacks dominate recent transaction count surge
In address poisoning scams, attackers distribute "dust" to thousands or millions of wallets, adding scam addresses that are similar to legitimate ones to transaction histories, often matching the beginning and ending characters. Dusts are tiny amounts of cryptocurrency in a wallet, often below $1.
"The victim sees a 'familiar' address in transaction history, copies it without full verification, and sends real funds to the attacker," wrote Sergeenkov.
He noted that 80% of recent growth in network activity is attributed to stablecoins, with 67% of that figure originating from wallets that received less than a dollar as their first stablecoin transaction. The analysis showed that 3.86 million out of 5.78 million addresses received poisoning dust as their first transaction.
To trace the source of these transactions, Sergeenkov focused on USDT and USDC transfers under $1, identifying at least 10,000 unique addresses that distributed dust. Most stemmed from smart contracts that automated the transfer of poisoning dust to hundreds of thousands of wallets via a transaction-batching function.
Attackers resumed the strategy on Ethereum, as the low-fee environment enabled by the Fusaka upgrade since early December has reduced the risk of losing significant funds to gas fees while conducting such attacks.
Ethereum Price Forecast: ETH falls below key ascending triangle, eyes $2,880 support
Ethereum declined below $3,000 on Tuesday, wiping out $265 million in leveraged positions, dominated by $249 million in long liquidations, in its futures market over the past 24 hours, per Coinglass data.
The move saw ETH break below the 20-day and 50-day Exponential Moving Averages (EMAs), as well as the lower boundary of an ascending triangle pattern extending from December 18.
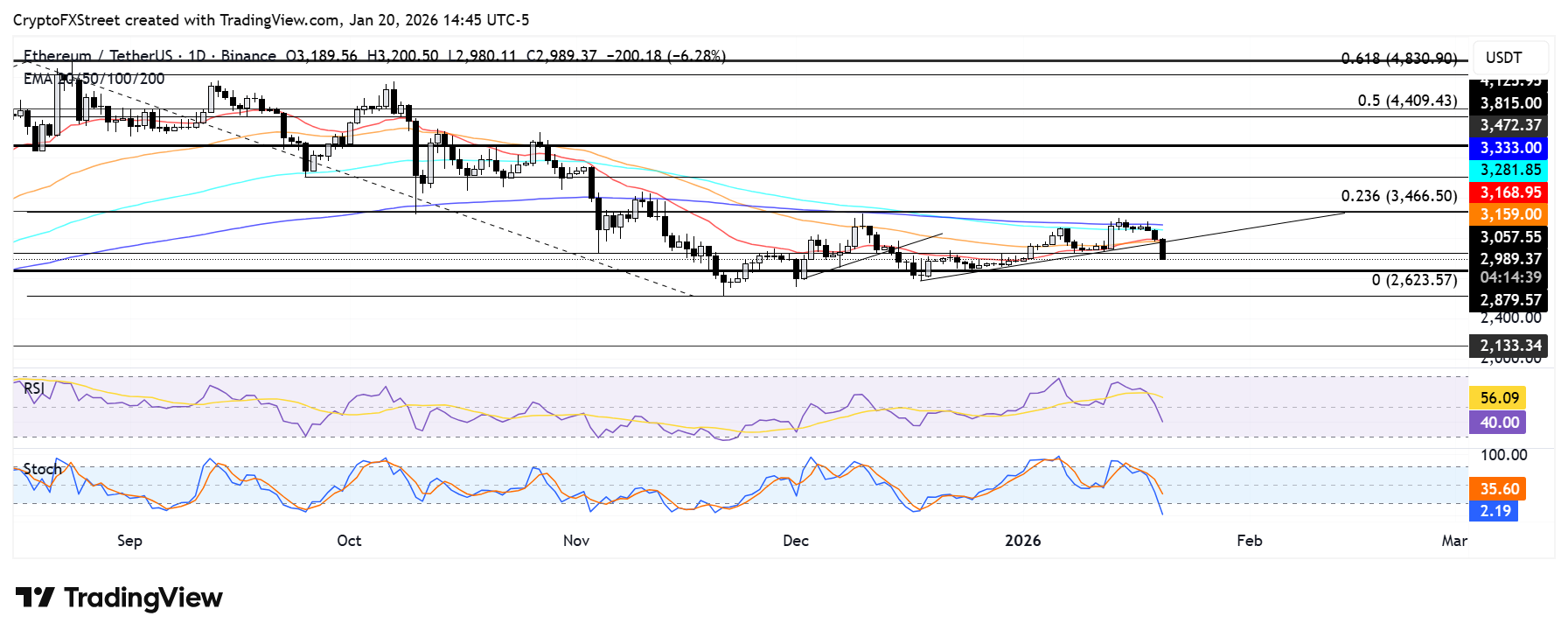
The top altcoin also breached the $3,057 support level. A failure to recover the support could see ETH test the $2,880 key level.
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) has fallen below its neutral level while the Stochastic Oscillator (Stoch) is in oversold territory, indicating a dominant bearish momentum. Oversold conditions in the Stoch could inspire a short-term recovery.




